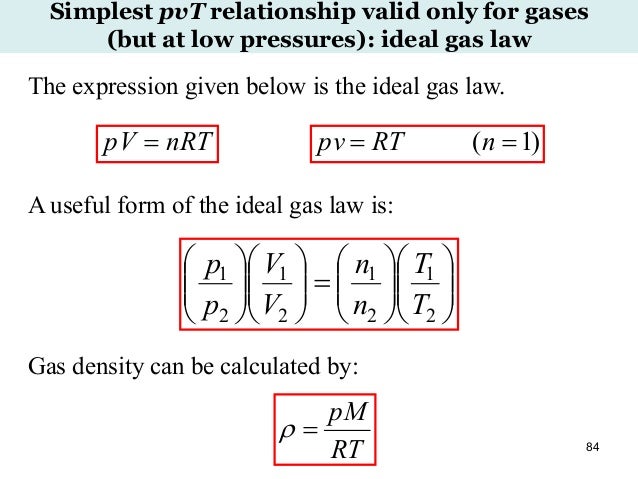
Pvt Relationship For Ideal Gas
= / For ideal gas.

Pvt relationship for ideal gas. #n# - the number of moles of gas;. The Relationship between Pressure and Volume As the pressure on a gas increases, the volume of the gas decreases because the gas particles are forced closer together. PV r = Constant Work Done in an Adiabatic Expansion Consider a mole of gas contained in a cylinder having insulating walls, provided with a frictionless and insulating piston.
Index Heat engine concepts. N = number of moles;. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 14 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law.
Explore diffusion and determine how concentration, temperature, mass, and radius affect the rate of. V/n = k = constant. The Ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas.
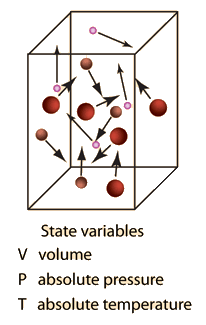
The impact of changes in temperature and number of moles is inversely preportional. Absolute pressure (P), volume (V), and absolute temperature (T). In this equation, p is the absolute pressure and V is the volume of a constant amount of gas in terms of either moles or mass.
A curve in a P-V diagram generated by the equation PV = const is called an isotherm. 0.006 liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. This is intended only as an introduction suitable for chemistry students at about UK A level standard (for 16 - 18 year olds), and so there is no attempt to.
As the PVT relationships of thermosets are still not well investigated by the industry, this model is the only PVT model supported in cases with thermoset material. The ideal gas equation makes some simplifying assumptions which are obviously not quite true. In the absence of an experimental data, the following methods may be used:.
PvT Surface for a Substance which Contracts Upon Freezing The equilibrium states of a simple, compressible substance can be specified in terms of its pressure, volume and temperature. The goal in defining heat capacity is to relate changes in the internal energy to measured changes in the variables that characterize the states of the system. Ideal gas laws demonstrate a relationship between volume, temperature and pressure for a combination of ideal gases.
What is the ideal gas law?. An ideal gas can be characterized by three state variables:. The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) relates the macroscopic properties of ideal gases.
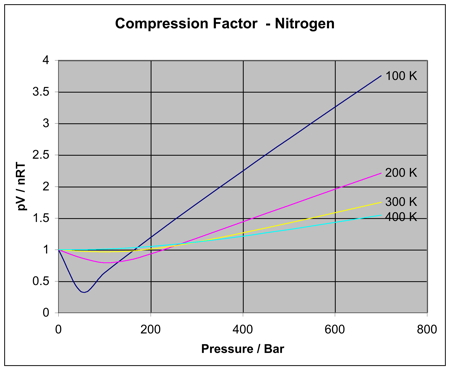
The system consists of an ideal gas. For an ideal gas, from the ideal gas law PV = NkT, PV remains constant through an isothermal process. At higher pressures, the use of the ideal gas equation of state may lead to errors as great as 500%, as compared to.
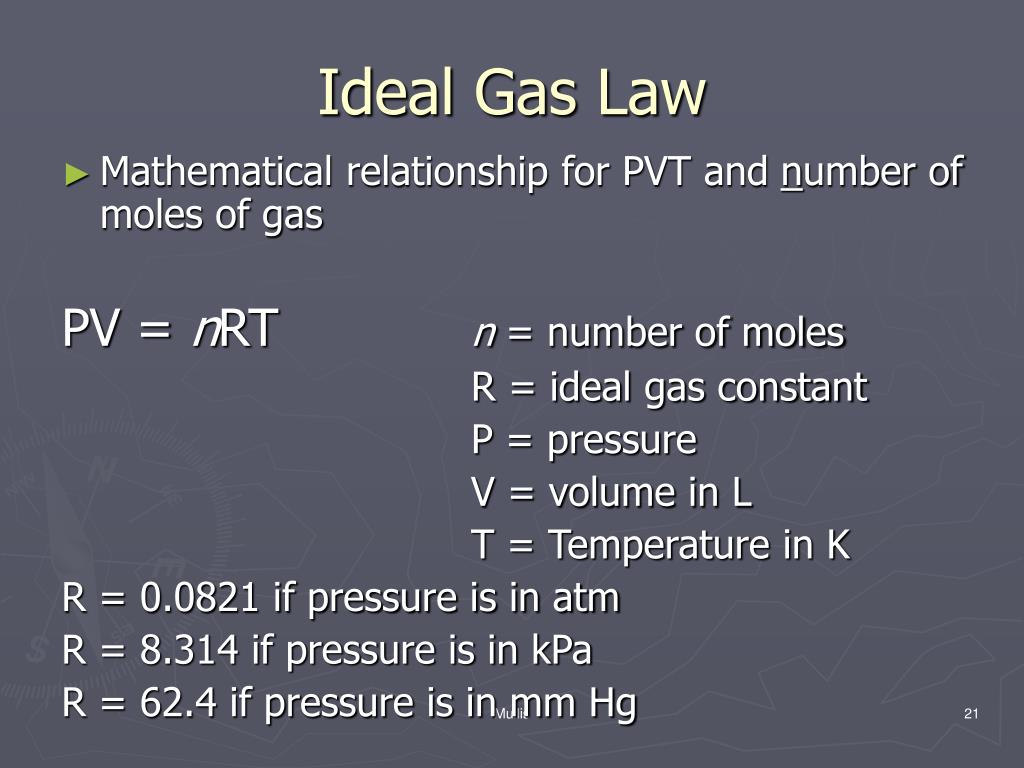
The relationship between them may be deduced from kinetic theory and is called the. This law states that:. P = pressure in pascals (unit Pa) V = volume in cubic metres (m 3) n = moles of gas (mol = mass in g / molecular mass of gas M r) R = ideal gas constant = 8.314 joules per kelvin per mol (J K-1 mol-1) T = temperature in kelvin (K).
PV = nRT In the formula, p represents the absolute pressure of the gas, V is the volume, n is the amount of the substance, R represents the gas constant ( 0.005 L atm / K mol), and T is the absolute temperature. From the equation q = n C ∆T, we can say:. The best method for obtaining the PVT relationship for a real gas is thru experimentation.
You will observe how ideal gas molecules behave according to the Ideal Gas Law, and you’ll learn about the relationship between pressure, volume and temperature in gases using gas thermometry. This value is equal to the change in enthalpy, that is, q P = n C P ∆T = ∆H. Similarly, at constant volume.
State Equations Reading Problems 6-4 → 6-12 The Thermodynamics of State IDEAL GAS The defining equation for a ideal gas is Pv T = constant = R Knowing that v = V/m PV Tm = constant = R where R is a gas constant for a particular gas (as given in C&B Tables A-1 and A-2). This is the currently selected item. On the right of the figure we have plotted the temperature versus the entropy of the gas.
2 - PVT Relationships for Real Gases (Computational Lab) Students doing this experiment are to check into the laboratory as usual with all the required data. Note that dU = m C V dT, C V = (R/MW)/ ( g -1), PV = nRT and dW = P dV. R = .01L atm/mol K.
Ideal gases and the ideal gas law This page looks at the assumptions which are made in the Kinetic Theory about ideal gases, and takes an introductory look at the Ideal Gas Law:. Ideal Bose equation of state. Engineering Sciences 36 Fall 17 Problem 4 The Ideal Gas Law Can Represent The Pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) Relationship Of Gases Only At Low (near Atmospheric Or Lower) Pressures.
Into the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature and the number of moles of a gas. In the following section, we will find how C P and C V are related, for an ideal gas. V is the volume of the ideal gas.
Define your temperature scale. • Derivation of P-V relation for adiabatic heating and cooling. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals) is an equation of state that generalizes the ideal gas law based on plausible reasons that real gases do not act ideally.The ideal gas law treats gas molecules as point particles that interact with their containers but not each other.
Then, you are free to leave. For a given mass of an ideal gas, volume is inversely proportional to pressure at constant temperature, i.e., v α 1 P (a t c o n s t a n t t e m p e r a t u r e) This equation is not rendering properly due to an. The behavior of ideal gases has been studied exhaustively and can been extensively described by mathematical relationships.
Although estimations using the ideal gas law are approximate, they are still close. Measure the temperature and pressure, and discover how the properties of the gas vary in relation to each other. In this experiment of measurement properties or PVT deals with ideal gas.
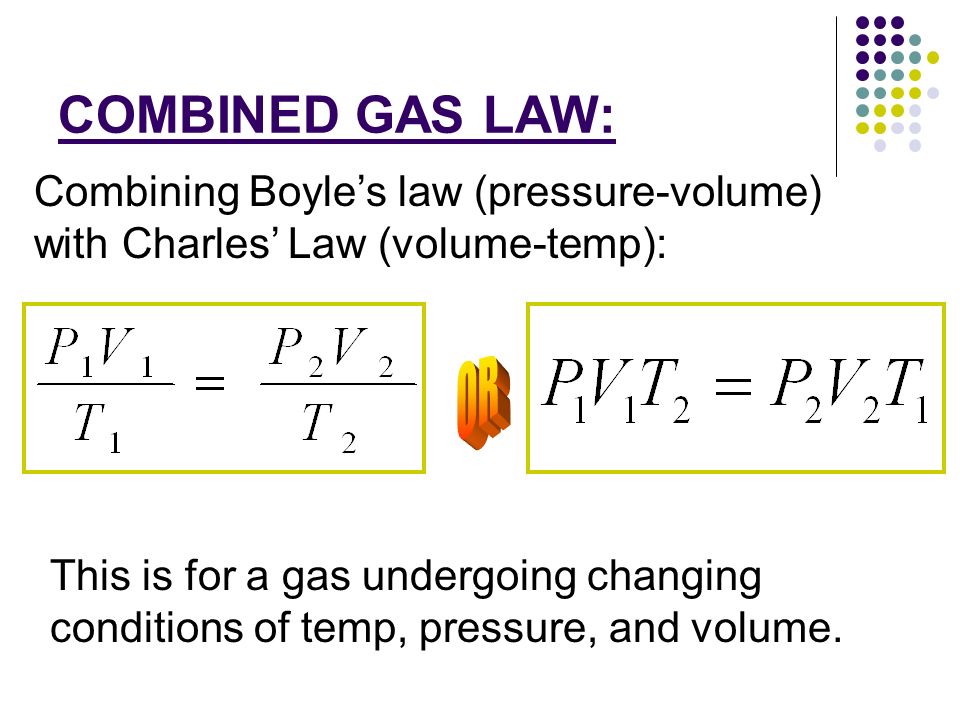
PV/nT = constant (T in Kelvins) P1V1/n1T1 = P2V2/n2T2. An ideal gas is a gas in which the particles (a) do not attract or repel one another and (b) take up no space (have no volume). Equations of State (EOS):These are correlation or physically based equations that relate Pressure, Volume, and Temperature that exist inside a material (typically gas).
Where p is the pressure, V the volume, n the number of moles, T the temperature, and R = 8.31 J/(mol·K) is the ideal gas constant. This model is derived from the ideal gas law by adding a pressure and temperature correction term to the specific volume. In this definition P and T are the absolute pressure and absolute temperature respectively and R is the particular gas constant which is R= 8.3145 J/mol.K and n is the number of moles of the gas filling the container.
(b) Just use the result from part (c ) along with the ideal gas equation to convert V to P. {\displaystyle pV_ {m}=RT~ {\frac { {\text {Li}}_ {\alpha +1} (z)} {\zeta (\alpha )}}\left ( {\frac {T} {T_ {c}}}\right)^ {\alpha }}. Gas is best explained by the “ideal gas law.” The formula for the ideal gas law demonstrates this relationship:.
Here you can visualize the ideal gas law, p·V = n R T. The Ideal Gas Constant R. In the Ideal Gas Law simulation, you will define the physical concept of temperature and absolute zero.
It is a good approximation to the behaviour of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. The P-V-T relationship of fluids is hard to formulate. Thus far, the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, has been applied to a variety of different types of problems, ranging from reaction stoichiometry and empirical and molecular formula problems to determining the density and molar mass of a gas.As mentioned in the previous modules of this chapter, however, the behavior of a gas is often non-ideal, meaning that the observed relationships between its.
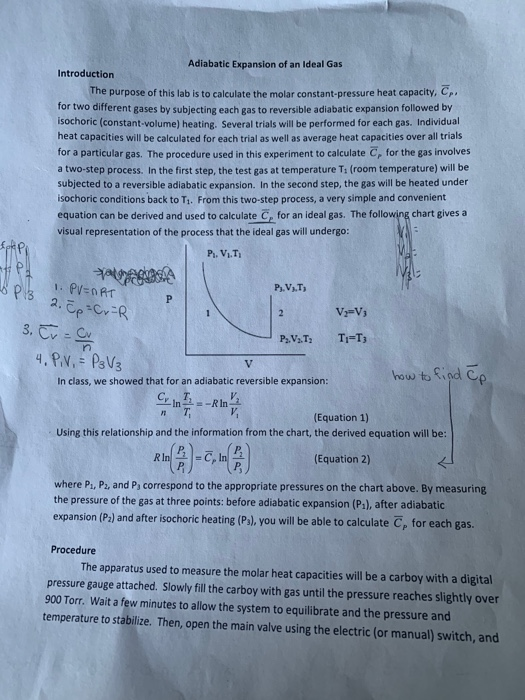
These three thermodynamic variables are easily measured and make up what is known as a PVT relationship. For Higher Pressures, More Complex Equations Of State Should Be Used. For an Adiabatic Process for an ideal gas is given by:.
Avagadro’s law for a fixed pressure and temperature, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of that gas. Ideal gas law the functional relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature and moles of a gas. 4 - Changes in kinetic and potential energies are negligible.
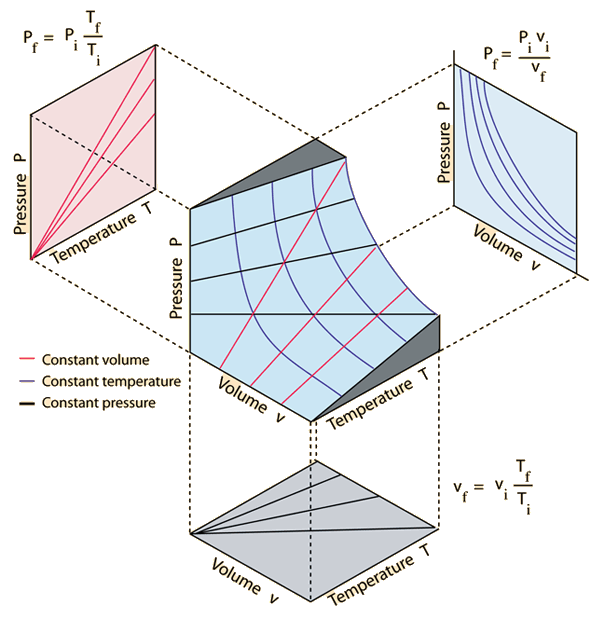
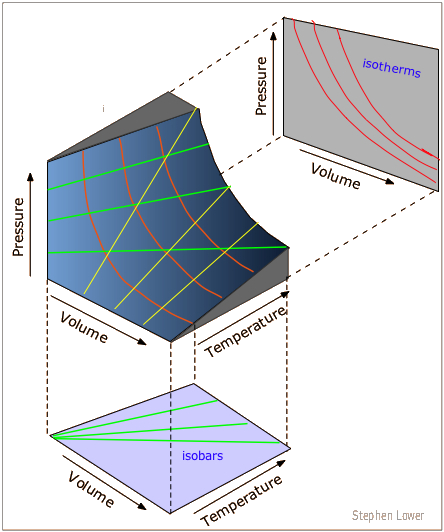
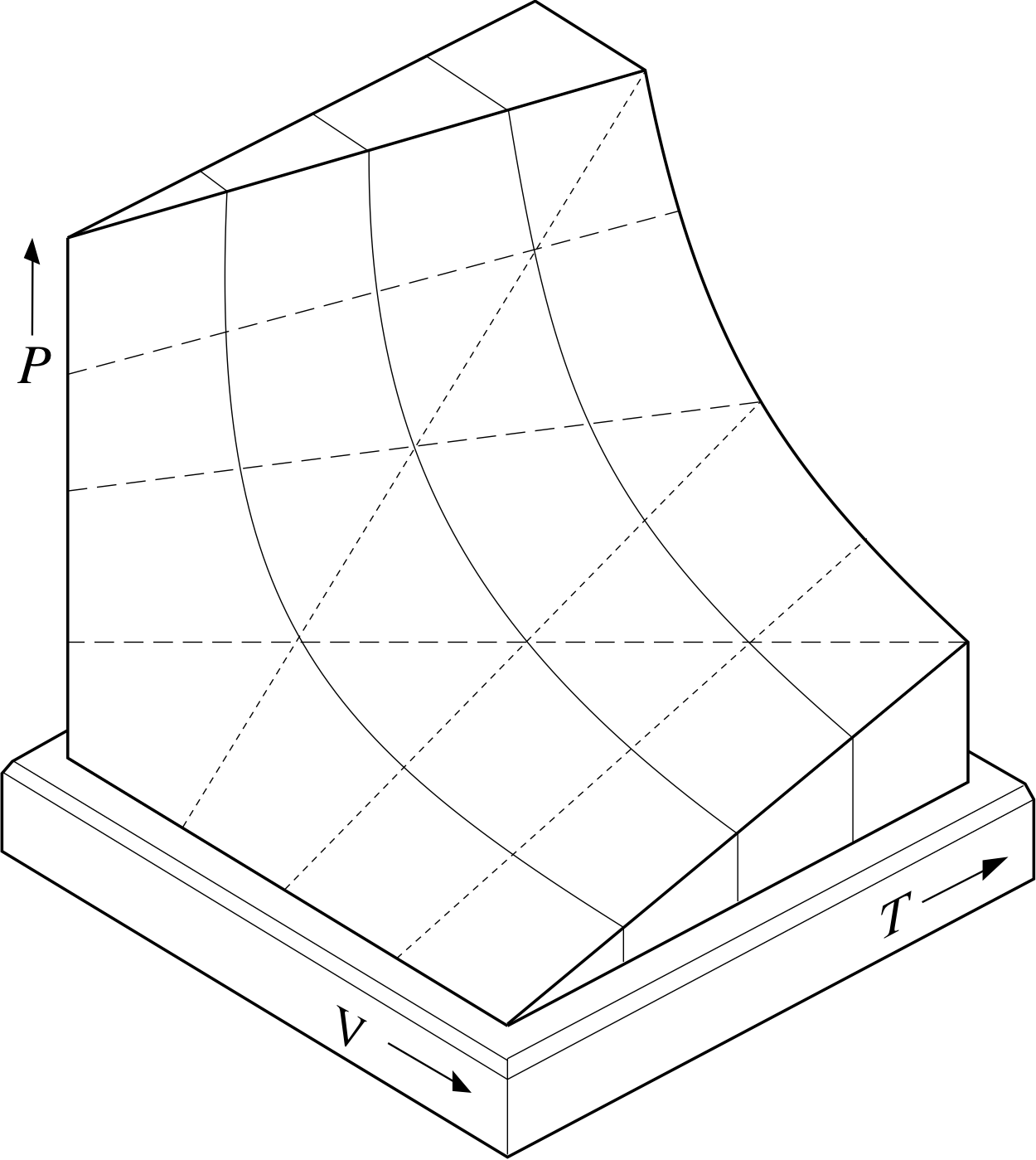
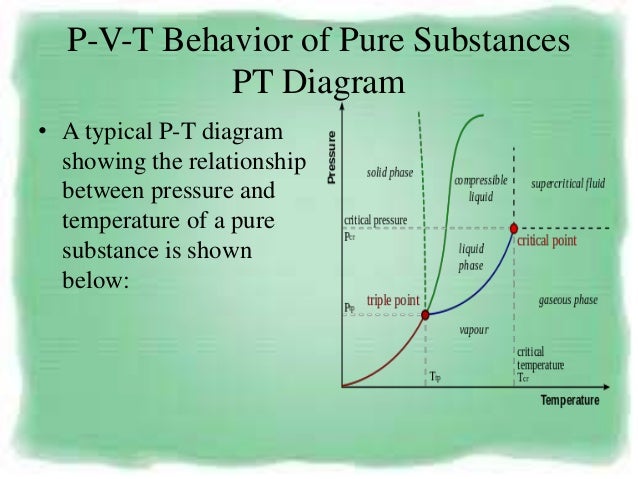
In order to depict the relations between the three variables P, V and T we need a three-dimensional graph. With the exception of some noble gases, such as helium and neon, the ideal gas law is not entirely accurate in describing these relationships. Examine kinetic energy and speed histograms for light and heavy particles.
The ∝ symbol means that the left side of the equation is proportional to the right side. An Isentropic Process for an Ideal Gas. You will arrive at the form (1/T) dT and (1/V) dV on both sides.
The ideal gases obey the ideal gas law perfectly. #PV = nRT#, where #P# - the pressure of the gas;. The ideal gas law allows us to calculate the value of the fourth variable for a gaseous sample if we know the values of any three of the four variables (P, V, T, and n).It also allows us to predict the final state of a sample of a gas (i.e., its final temperature, pressure, volume, and amount) following any changes in conditions if the parameters (P, V, T, and n) are specified for an initial.
R = universal gas constant = 8.3145 J/mol K N = number of molecules. Observe the atom motions in one panel;. Each point on the curved surface represents a possible combination of (P,V,T) for an arbitrary quantity of an ideal gas.
5 - Boundary work is the only type of work that crosses the system boundary. Notice that the particles do not interact with one another. Kelvin scale and Ideal gas law example.
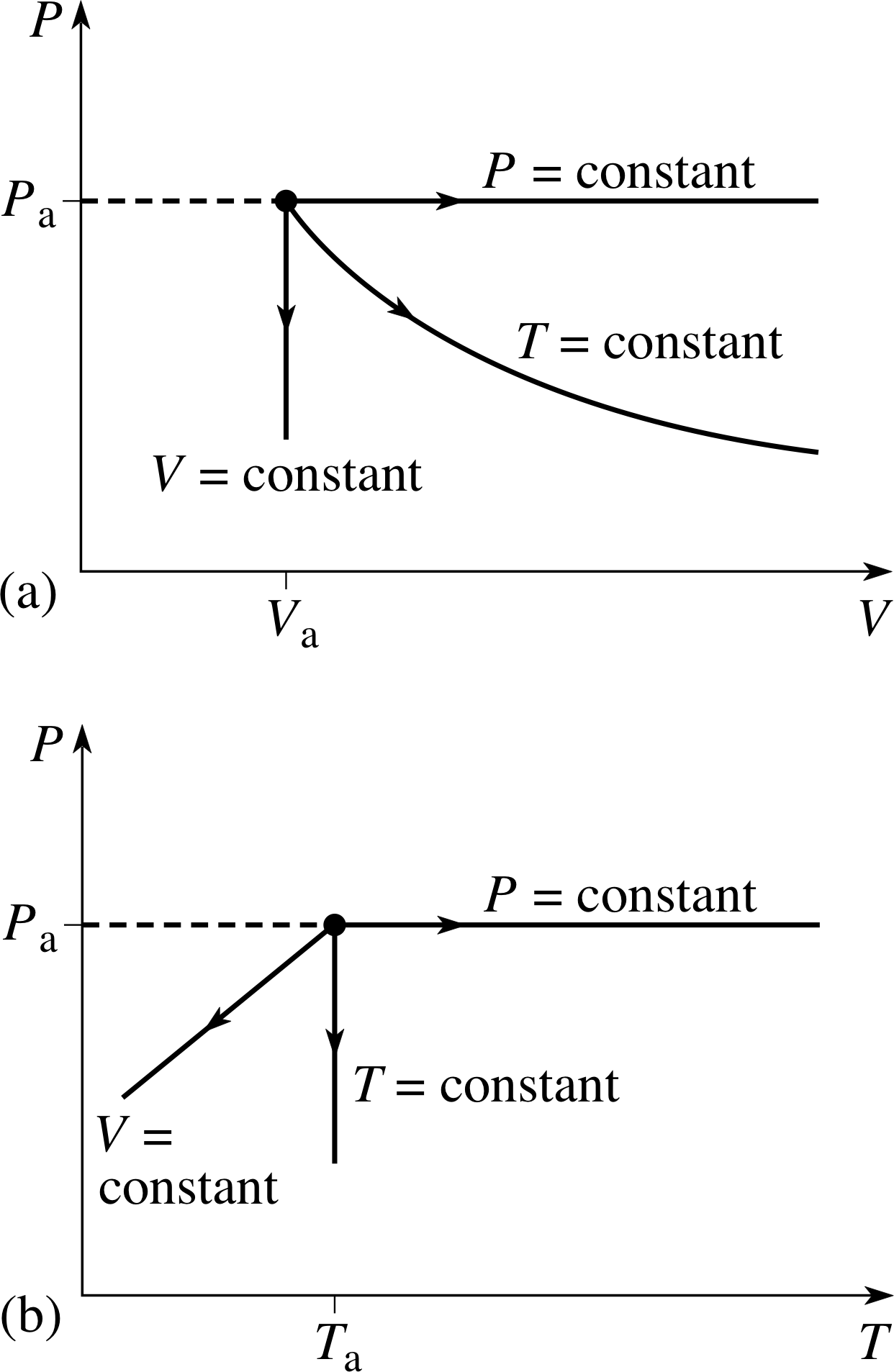
Thermodynamics - Thermodynamics - Heat capacity and internal energy:. A PVT relationship is one of the forms of the equations of state (see Equations of State), which relates the pressure, molar volume V and the temperature T of physically homogeneous media in thermodynamic equilibrium. If any two of these state variables is specified, the third is determined.
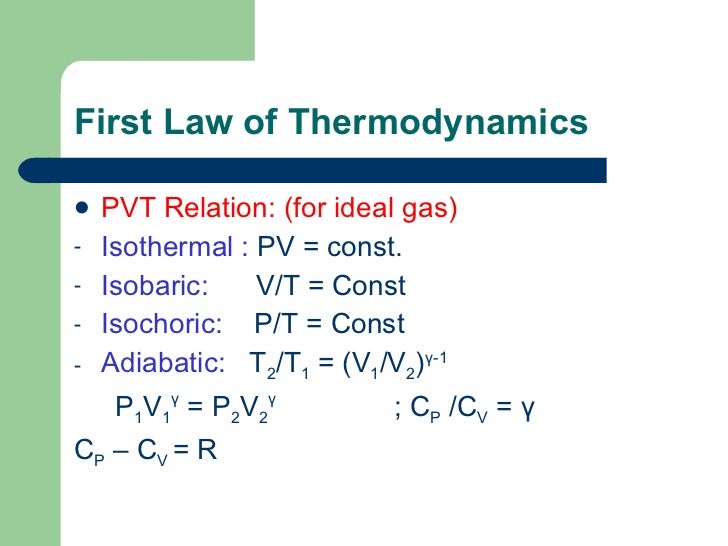
The Ideal Gas Law:. Gay-Lussac’s/Avogadro’s Law of Combining Volumes. The ratio of the specific heats γ = C P /C V is a factor in determining the speed of sound in a gas and other adiabatic processes as well as this application to heat engines.
The volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the number on moles of gas, directly proportional to the temperature and inversely proportional to the pressure. Submit the pre-lab (an outline of what you will be doing). All gases are ideal at low pressure.
PVT relationships, standard deviation EQUIPMENT:. Think of this symbol as a “proportionality” symbol instead of an “equals” symbol. In the other panel observe averages for the pressure at different settings for the temperature and density.
The equation of state for an ideal Bose gas is. 2 - The specific heat ratio is constant (required in part (b) only). P V m = R T Li α + 1 ( z ) ζ ( α ) ( T T c ) α.
Ideal Gas PVT Measurement. Represent the PVT behavior of most gases up to a P of 15bar. Where, P is the pressure of the ideal gas.
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas.It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. The word fluid covers both gases and liquids, any gas and any liquid is a. Moles and the ideal gas law.
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the van der Waals equation (or van der Waals equation of state;. Pump gas molecules to a box and see what happens as you change the volume, add or remove heat, and more. The pressure and volume of a gas will change in direct preportion to each other.
As described on the work slide, the area under a process curve on a p-V diagram is equal to the work performed by a gas during the process. The relationship between C P and C V for an Ideal Gas. 3 - The cycle is executed in a closed system ( not required, but it makes the solution simpler).
Equal volumes of any gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of moles of. For a system consisting of a single pure substance, the only kind of work it can do is atmospheric work, and so the first law reduces to dU = d′Q − P dV. Tarek Ahmed PhD, PE, in Equations of State and PVT Analysis (Second Edition), 16.
At constant pressure P, we have. For an isothermal, reversible process, the work done by the gas is equal to the area under the relevant pressure -volume isotherm. In order for two variables to have a direct relationship, they must increase or decrease at the same rate.
An ideal gas is a gas that obeys the relationship PV=nRT. The Calculation Of The Molar Volume And The Compressibility Factor, Z-defined As Z Using Complex. Since at constant temperature, the entropy is proportional to the volume, the entropy increases in this case, therefore this process is irreversible.
Molar ideal gas law problem. Equations of State 3. Behavior of Real Gases.
In dealing with gases at a very low pressure, the ideal gas relationship is a convenient and generally satisfactory tool. The ideal gas equation can be written as. This plot is called a T-s diagram.
• For an ideal gas, the temperature remains constant because the internal energy only depends on temperature in that case. And, sign up the interview sheet. This ratio γ = 1.66 for an ideal monoatomic gas and γ = 1.4 for air, which is predominantly a diatomic gas.
Conversely, as the pressure on a gas decreases, the gas volume increases because the gas particles can now move farther apart. Q P = n C P ∆T. As an ideal model it serves as a reference for the behavior of real gases.
Apply the 1st Law to step 2-3. In other words, two variables. #V# - its volume;.
This applet allows you to measure the pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) relationship for an ideal gas. No gas is truly ideal, but the ideal gas law does provide a good approximation of real gas behavior under many conditions. Integrate to obtain the desired result.
The equation, known as the ideal gas equation, is given as:. #R# - the gas constant, usually given as #0.0("atm" * "L")/("mol" * "K")# #T# - the temperature of the gas. PVT surface for an ideal gas.
The ideal gas equation (PV=nRT) provides a valuable model of the relations between volume, pressure, temperature and number of particles in a gas.
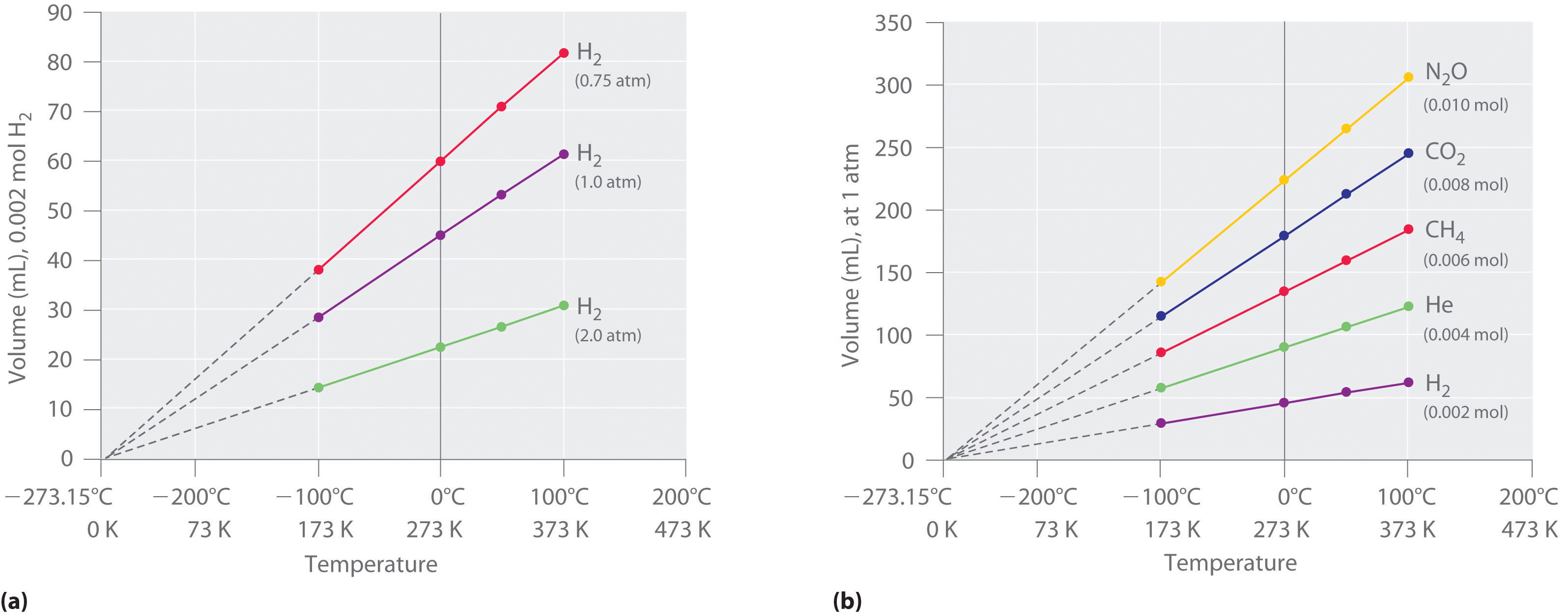
Relationships Among Pressure Temperature Volume And Amount

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11

P V T Surface In Thermodynamics Mechanical Engineering Concepts And Principles
Pvt Relationship For Ideal Gas のギャラリー

1 The Ideal Gas 2 Ideal Gas Equation Of State Property Tables Provide Very Accurate Information About The Properties It Is Desirable To Have Simple Ppt Download

Pvt Relationships For Real Gases Gases Pressure
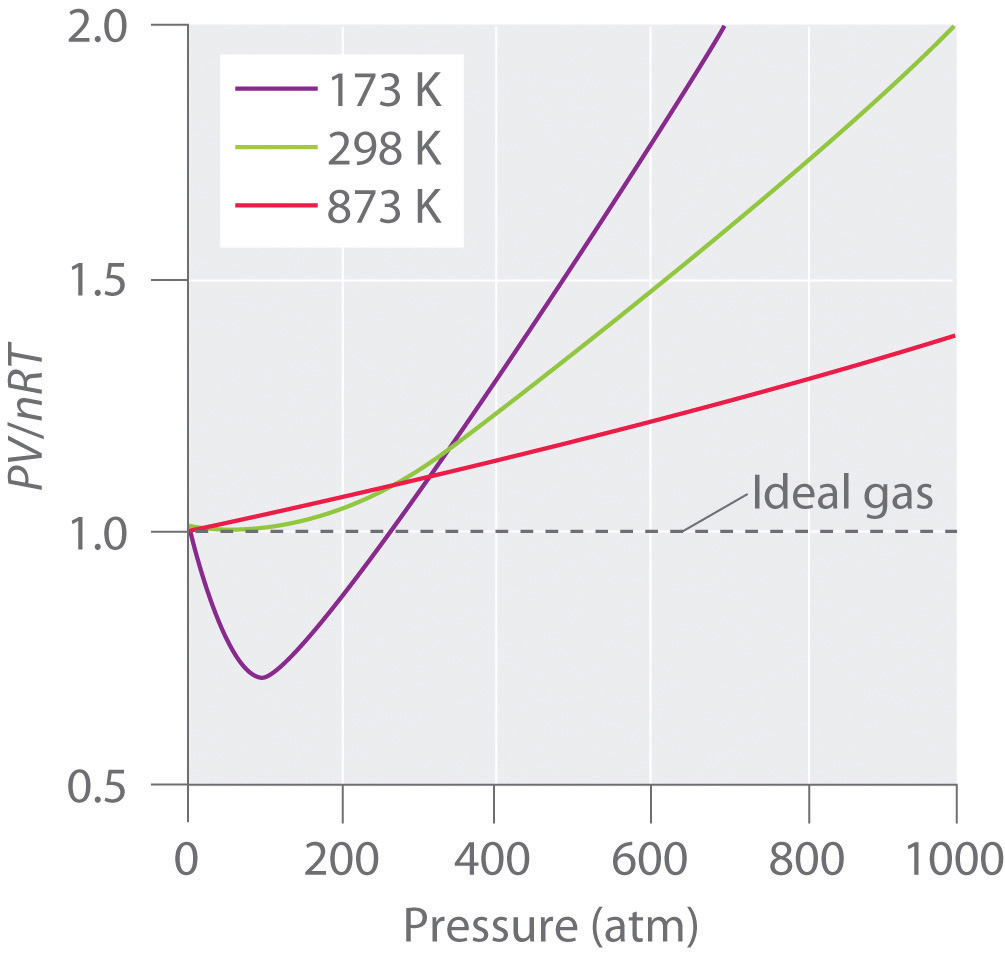
The Behavior Of Real Gases
Ideal Behavior Png 5 Phase Behavior Of Natural Gas And Condensate Fluids

Van Der Waals Equation Wikipedia

Equation Of State Wikipedia
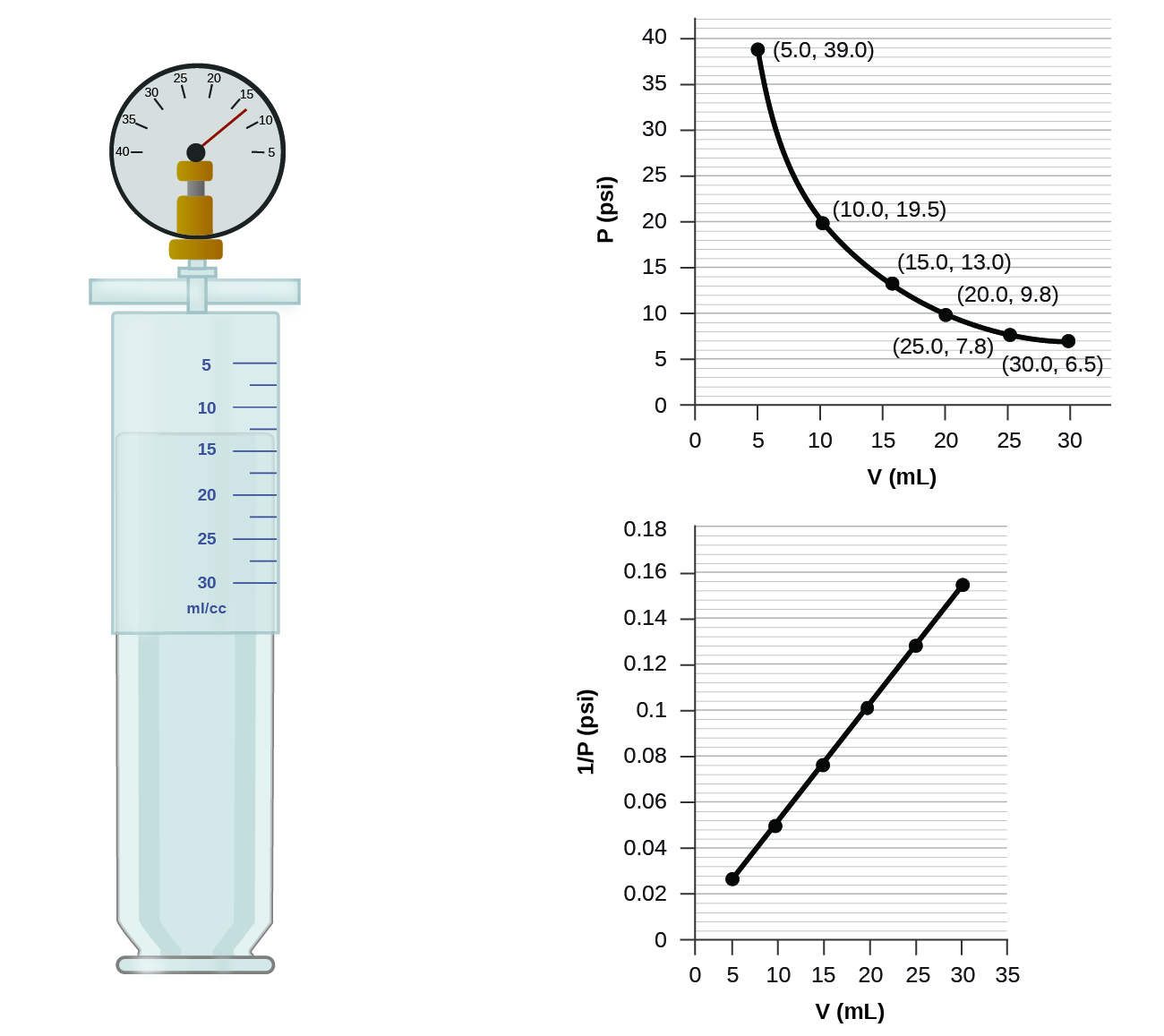
9 2 Relating Pressure Volume Amount And Temperature The Ideal Gas Law Chemistry

Ppt Thermodynamic Properties Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5036

Ideal Gas Graph Sketching

Pdf Chapter 18 Heat And The First Law Of Thermodynamics Conceptual Problems Ana Claudia Academia Edu
Ideal Gas Law

Relation Between P V T For An Ideal Gas Undergoing Adiabatic Chan

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11

How To Do P V T Pressure Volume Temperature Gas Calculations Formula Boyle S Law Charles S Law Gay Lussac S Law Ideal Gas Behaviour Problem Solving Revision Examples Graphs Gcse Chemistry Physics Ks4 Science A
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqxc2jdulbxwjdyl4anhx2kkmdyeccippt0vbm5cm2tir6xj8 Usqp Cau

Non Ideal Behavior Of Gases Article Khan Academy
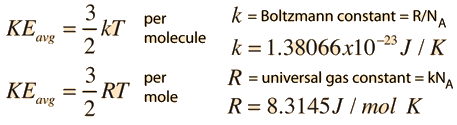
Ideal Gas Law
Ideal Gas Law

Solved 7 The O Gas Masses In A Tank Of Capacity 42l A Chegg Com

1 Equations Of State The Relationship Among The State Variables Temperature Pressure And Specific Volume Is Called The Equation Of State We Now Consider Ppt Download
Pplato Flap Phys 7 4 Specific Heat Latent Heat And Entropy
Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 31 July 16
Is Nitrogen An Ideal Gas Why Or Why Not Quora
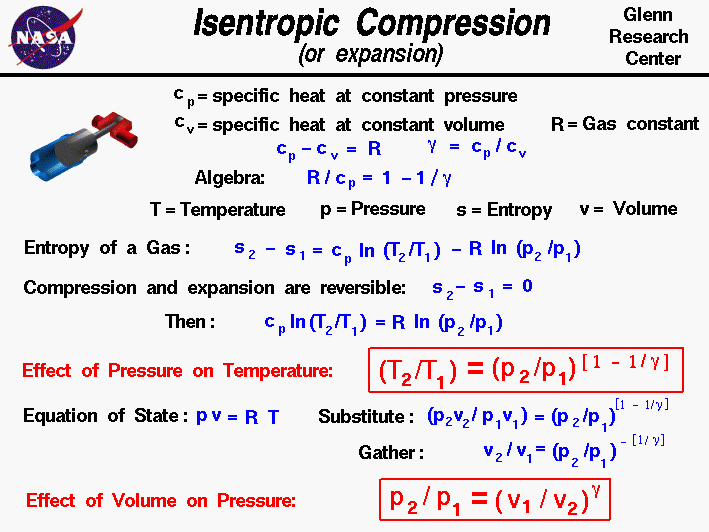
Isentropic Compression Or Expansion

How To Do P V T Pressure Volume Temperature Gas Calculations Formula Boyle S Law Charles S Law Gay Lussac S Law Ideal Gas Behaviour Problem Solving Revision Examples Graphs Gcse Chemistry Physics Ks4 Science A

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsunlqupczp9hjixftndyxv 7hq6ldrbupub9bggpkii3e Nh Q Usqp Cau

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11
Ideal Gases Ib Physics Stuff

Gas Laws Boyle S Law Charle S Law Gay Lussac S Law Avogadro S Law

Gas Laws
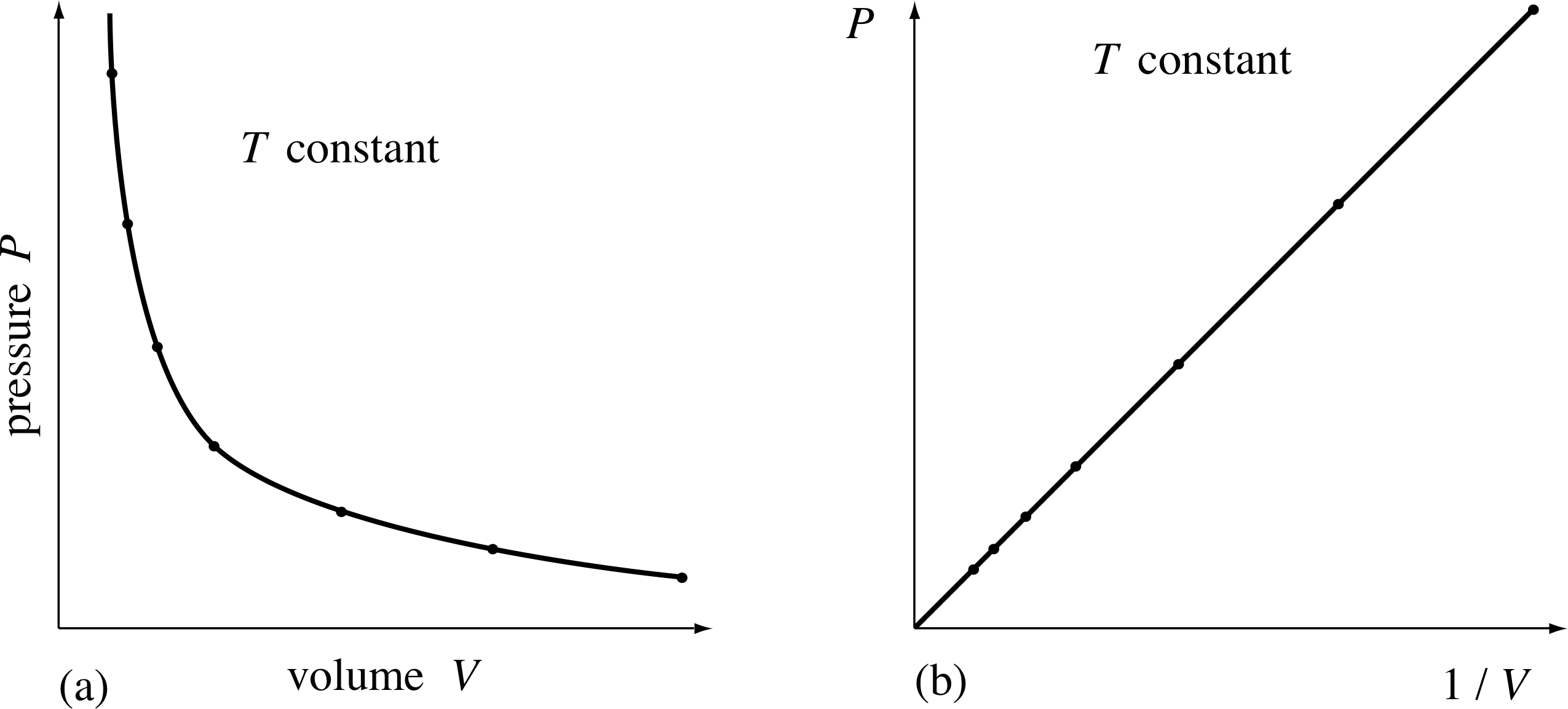
Pplato Flap Phys 7 2 Temperature Pressure And The Ideal Gas Laws

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11
Thermal Engineering Relation Between Pvt

Ideal Gas Model For Many Gases The Ideal Gas Assumption Is Valid And The P V T Relationship Can Be Simplified By Using The Ideal Gas Equation Of State Ppt Download
Revision On Thermodynamics

1 Equations Of State The Relationship Among The State Variables Temperature Pressure And Specific Volume Is Called The Equation Of State We Now Consider Ppt Download
The Ideal Gas Equation

Ch18 Ssm

Chapter 2b Pure Substances Ideal Gas Updated 1 17 11

Gas Laws

Demo Cyclic Relation Using Ideal Gas Equation Youtube

Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook
Solved Derive Equation 2 From Equation 1 Other Known Equt Chegg Com

Real Gases Using The Van Der Waals Equation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

1 Evaluate The Following Partial Derivatives As A Chegg Com

Solved 4 Consider The Relationship Of Ideal Gas Pv 0 7t Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrhos5pxf Gcqbxtl91ya6ajrsbkugwgqrzzwwt35rmbj 59gqf Usqp Cau

Phase Changes Physics

Solved Develop A General Relationship For The Change In T Chegg Com

Solved Engineering Sciences 36 Fall 17 Problem 4 The Id Chegg Com

Chapter 5 A A A Single Phase Systems A Aˆa

Equation Of State Wikipedia

The Gas Laws Statements Formulae Solved Problems
6 2 Ideal Gas Model The Basic Gas Laws Chemistry Libretexts

Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations

Adiabatic Process P V T Relation Youtube

Rmp Lecture Notes

Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations

Pptx Thermodynamic Applied And Interdisciplinary Physics Continuum Mechanics

Ideal Gas Equation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Real Gases
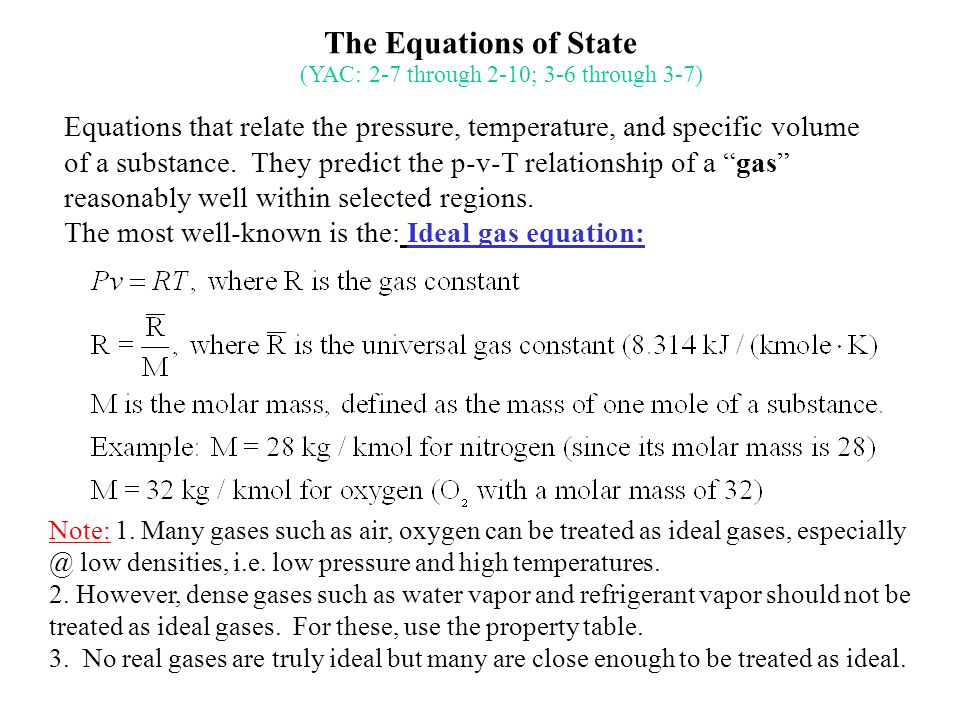
The Equations Of State Yac 2 7 Through 2 10 3 6 Through 3 7 Ppt Video Online Download
Equation Of State For Non Ideal Gases
Q Tbn 3aand9gcspcligjfybcmci22esegzqz5rhiu7mjz4lhf2zzvo O Guoa4n Usqp Cau

Pvt Surface For An Ideal Gas Download Scientific Diagram
The Gas Laws Definition Formula Examples Studiousguy

Polytropic Processes For An Ideal Gas Youtube

How To Do P V T Pressure Volume Temperature Gas Calculations Formula Boyle S Law Charles S Law Gay Lussac S Law Ideal Gas Behaviour Problem Solving Revision Examples Graphs Gcse Chemistry Physics Ks4 Science A

Ideal And Real Gases Thermodynamic Relations

Gas Laws

Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmuuavcsj6ln2isyzghu7e7i8wwyneooet3g Usqp Cau
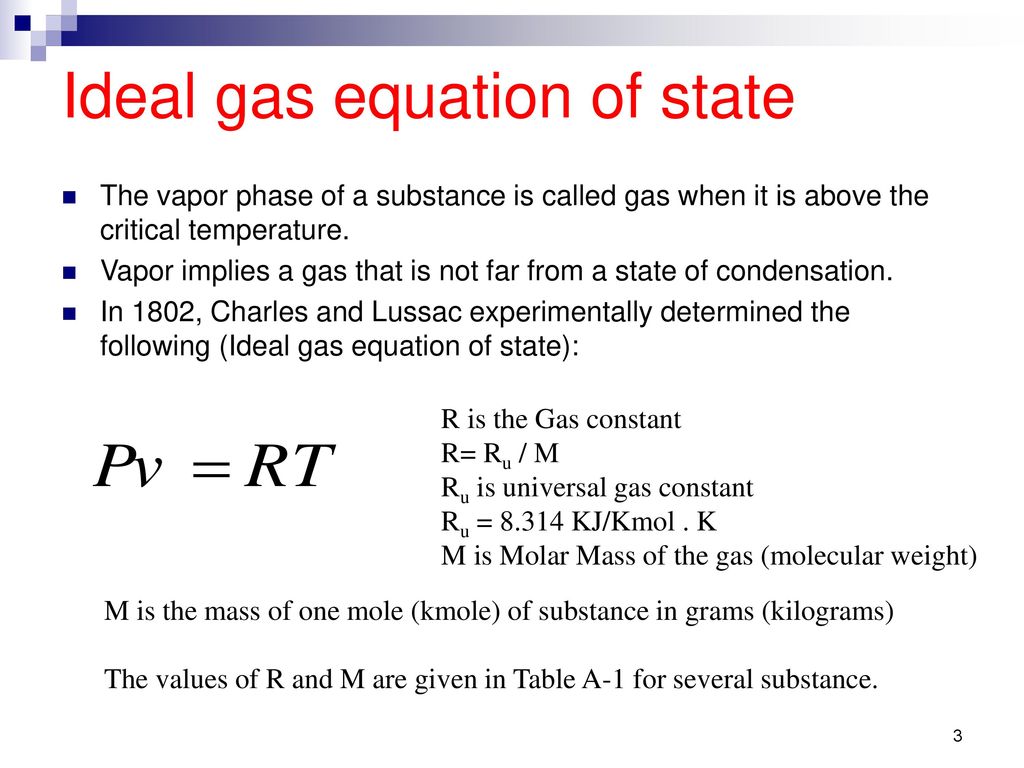
The Ideal Gas Ppt Download
Pplato Flap Phys 7 2 Temperature Pressure And The Ideal Gas Laws
Ppt Characteristics Of Gases Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 435

The Equations Of State Equations That Relate The Pressure Temperature And Specific Volume Of A Substance They Predict The P V T Relationship Of A Gas Ppt Download
Equation Of State Wikipedia
Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations

Pvt Surface For An Ideal Gas Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www Sfu Ca Mbahrami Mech 240 Lectures Ideal gas equation of state Pdf
Notes Combined And Ideal Gas Laws Ppt Download
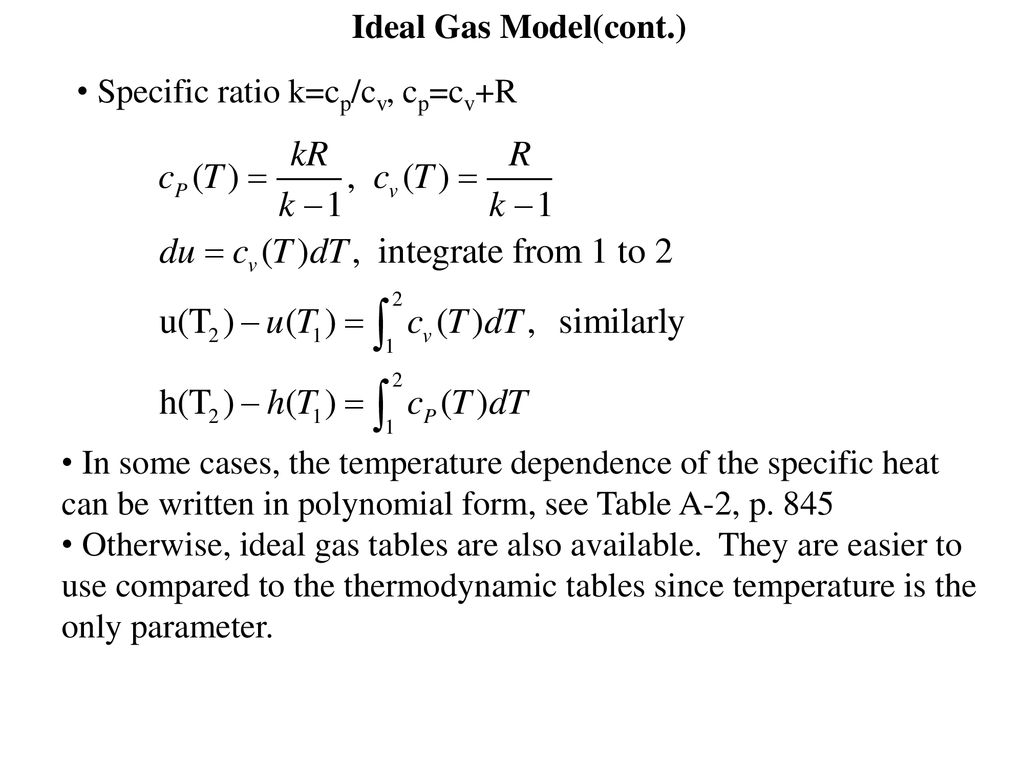
Ideal Gas Model For Many Gases The Ideal Gas Assumption Is Valid And The P V T Relationship Can Be Simplified By Using The Ideal Gas Equation Of State Ppt Download
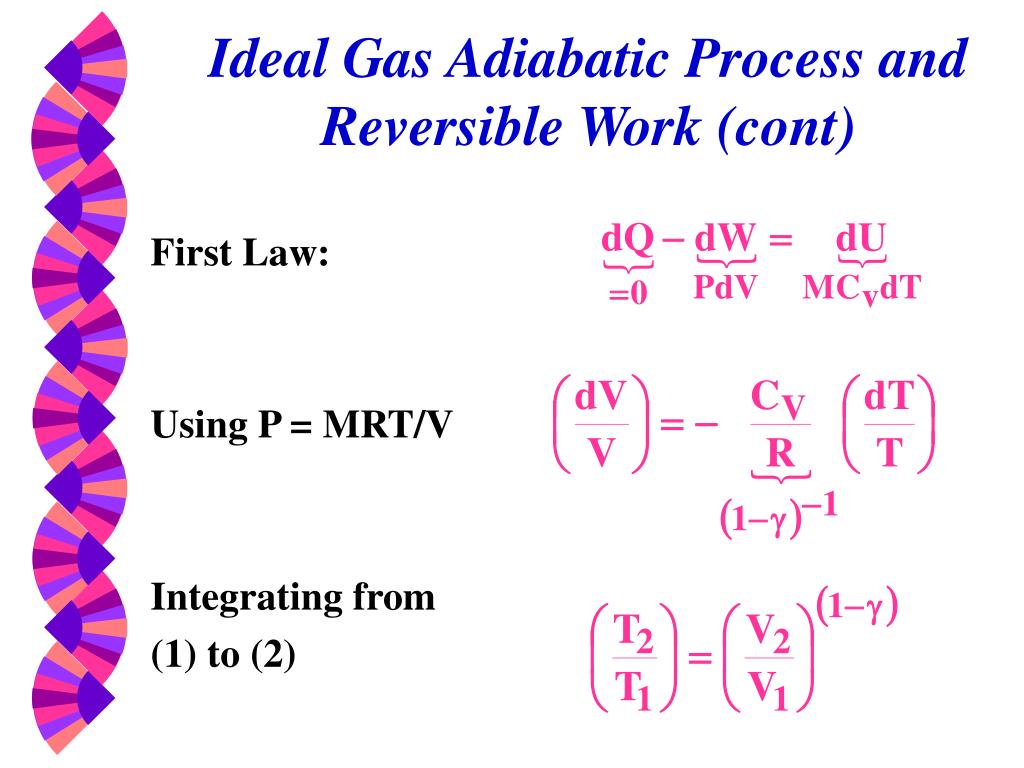
Ppt Thermodynamic Properties Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5036

Chap6 Single Phase Skf1113 1011 2 Chemical Engineering Studocu

Pressure Volume And Temperature Relationships Chemistry Tutorial Youtube

Thermal Engineering Relation Between Pvt
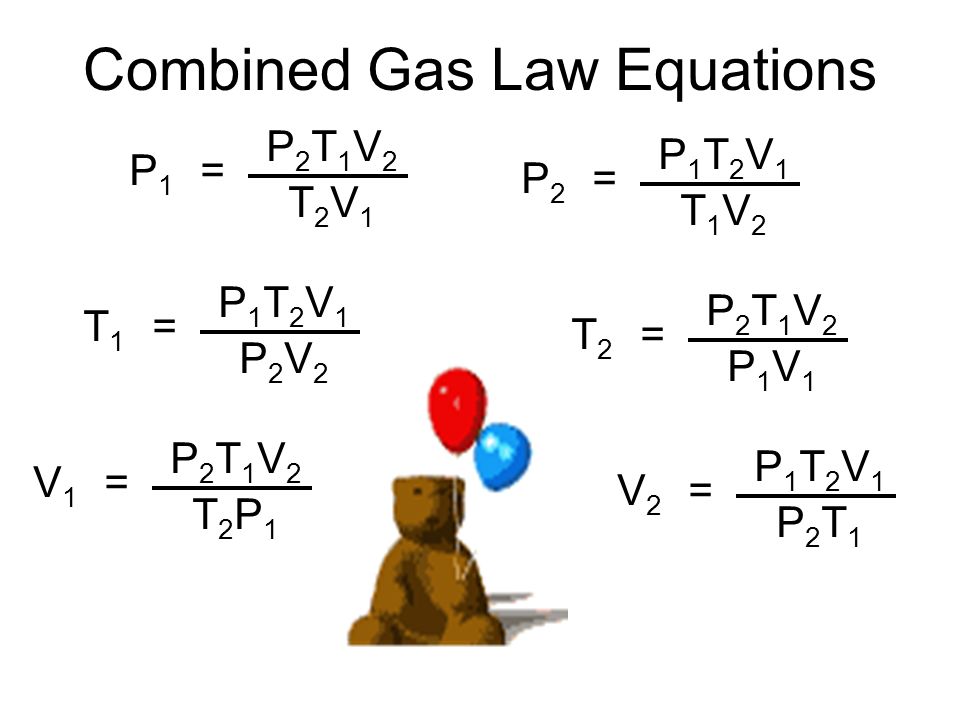
Gas Laws

Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Heat
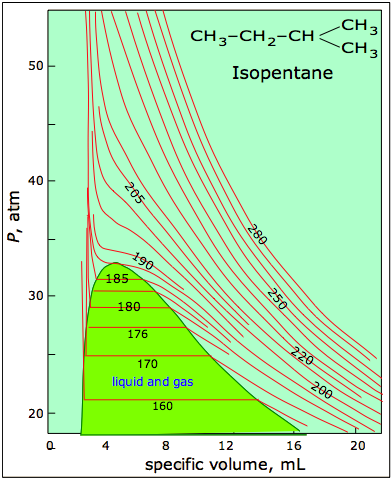
6 6 Real Gases And Critical Phenomena Chemistry Libretexts
Http Www Cabrillo Edu Jmccullough Physics4c Files 4c Sample Lab3 Pdf
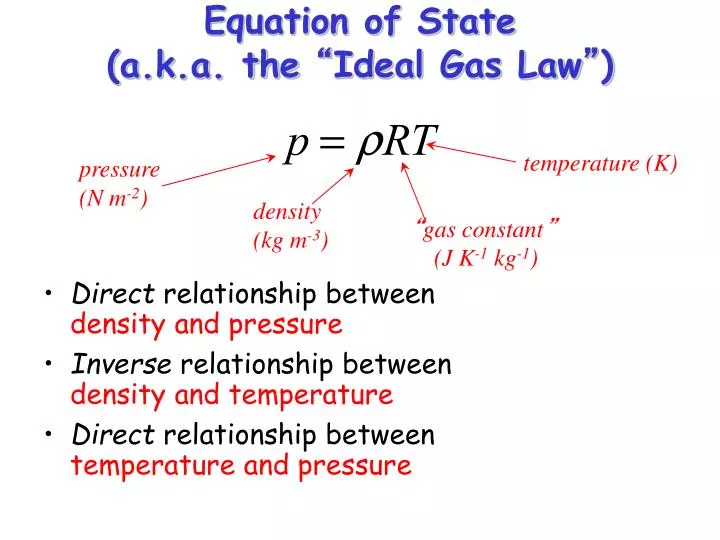
Ppt Equation Of State A K A The Ideal Gas Law Powerpoint Presentation Id

Chapter7 Lesson E Pvt Relationships For Isentropic Ig Processes
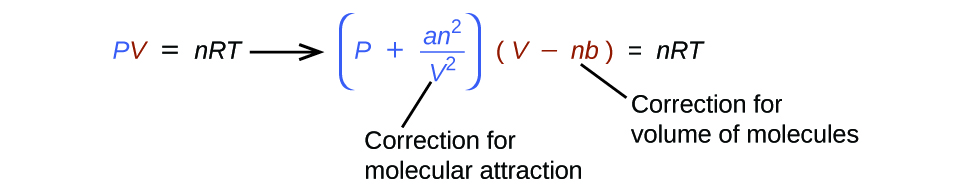
9 6 Non Ideal Gas Behavior Chemistry Libretexts

How Do We Sketch Pressure Against Pv T Where P Is Pressure V Is Volume And T Is Temperature Quora

Isentropic Process Nuclear Power

Proof Of Pressure Volume And Temperature Ratio Adiabatic Process Youtube

Thermal Engineering Relation Between Pvt
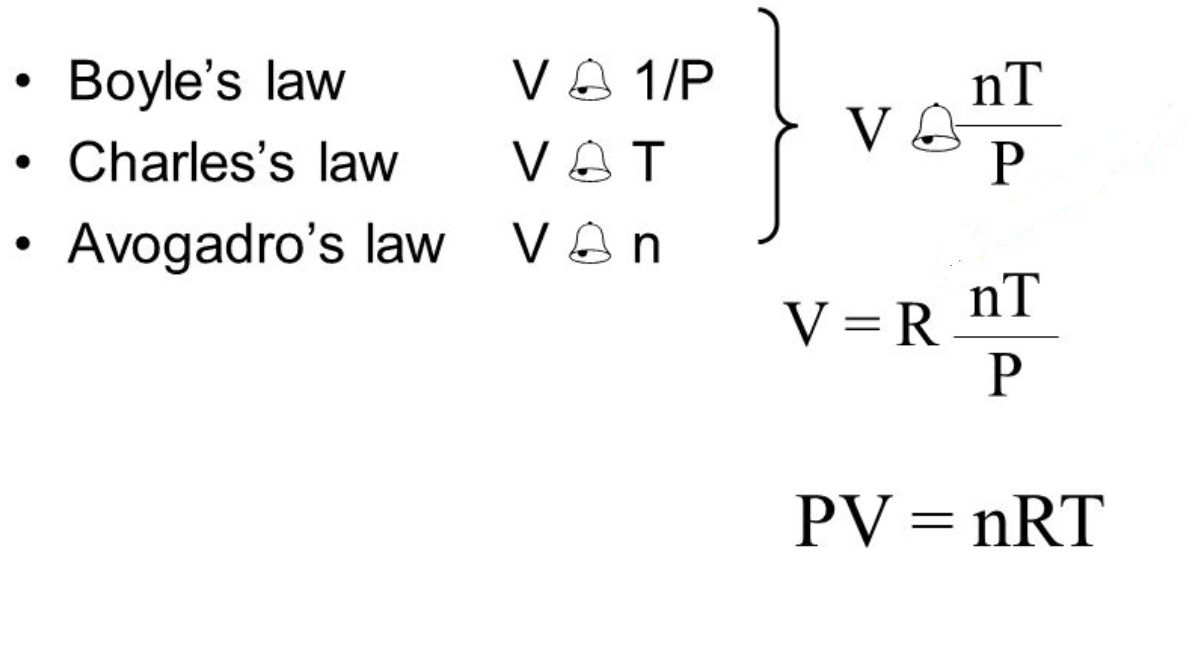
Gas Laws
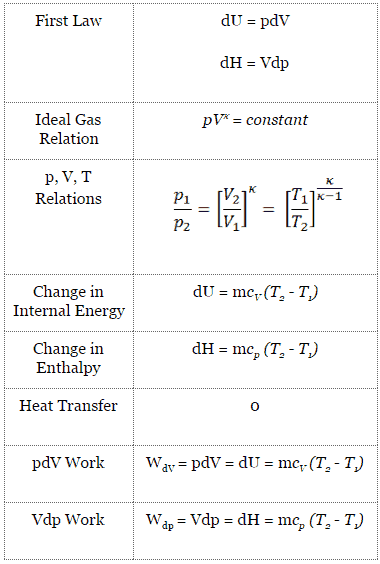
What Is Adiabatic Process Definition
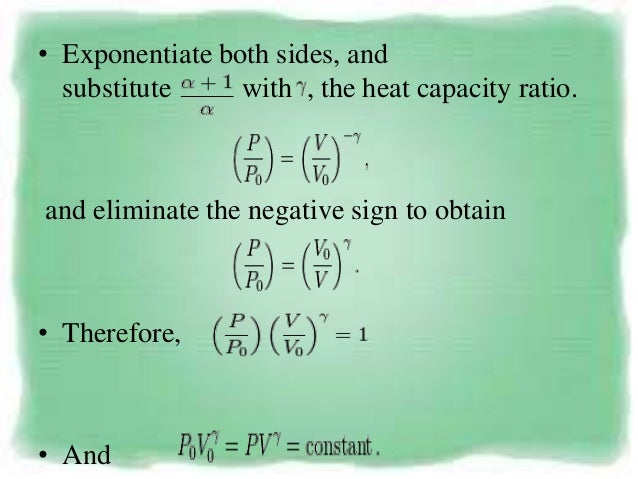
Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations
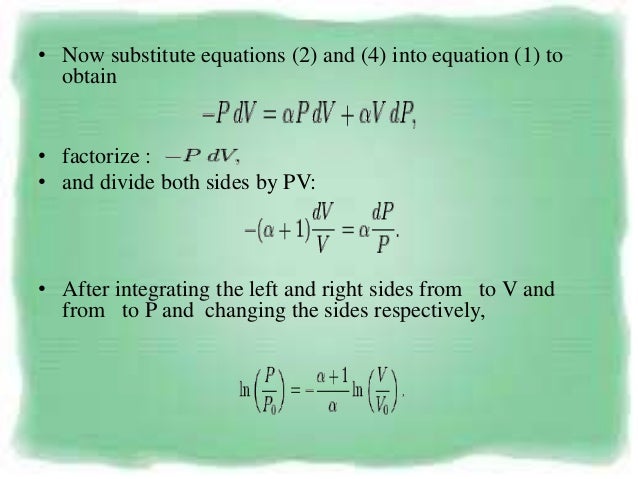
Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations



